搜索结果: 1-15 共查到“海洋科学 South China Sea”相关记录21条 . 查询时间(1.64 秒)
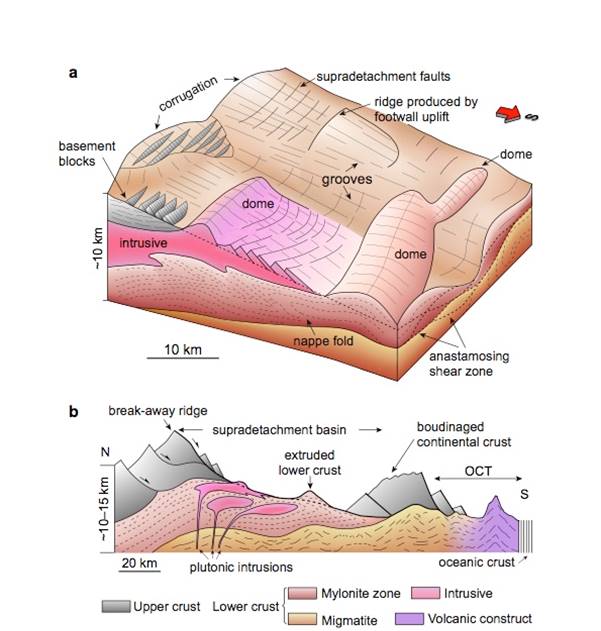
中国地质大学科学技术发展院邓洪旦*,任建业 等,海洋学院. Nature Communications(2020), South China Sea documents the transition from wide continental rift to continental break up(图)
三维;高清;地震数据;南海北部;被动陆缘大型;拆离;断层
2021/10/15
近日,中国地质大学海洋学院邓洪旦博士和任建业教授在国际著名科学期刊《Nature Communications》发表题为“South China Sea documents the transition from wide continental rift to continental break up”的学术论文。
中国地质大学科学技术发展院孙启良* 等,海洋学院,GSA Bulletin(2020),Post-rift magmatism on the northern South China Sea margin
南海北部;裂后期;岩浆活动;时间;控制因素;岩浆系统;三维结构
2021/10/15
近日,中国地质大学海洋学院孙启良教授在国际地学领域期刊《Geological Society of American Bulletin》发表了题为《南海裂后期岩浆活动》的学术论文,该文阐释了南海北部裂后期岩浆活动时间、控制因素和岩浆系统的三维结构等。孙启良教授为第一兼通讯作者,合作者包括中国地质大学海洋学院解习农教授以及来自英国加里夫大学的Tiago Alves教授、中科院南海所赵明辉研究员、法国...
Corals Die as Global Warming Collides with Local Weather in the South China Sea
Corals Die Global Warming Collides Local Weather South China Sea
2017/3/30
In the South China Sea, a 2°C rise in the sea surface temperature in June 2015 was amplified to produce a 6°C rise on Dongsha Atoll, a shallow coral reef ecosystem, killing approximately 40 percent of...
A History of Taiwan/US Oceanographic Research in the South China Sea
History of Taiwan/US Oceanographic Research South China Sea
2015/7/13
Oceanography is a relatively new field in Taiwan. As a maritime nation surrounded by water, the societal need to understand the seas has long been recognized. From the path of the Kuroshio to the path...
Turbulent Properties of Internal Waves in the South China Sea
Turbulent Properties Internal Waves South China Sea
2015/7/13
Luzon Strait and South China Sea waters are among the most energetic internal wave environments in the global ocean. Strong tides and stratification in Luzon Strait give rise to internal waves that pr...
Modeling and Prediction of Internal Waves in the South China Sea
Modeling and Prediction Internal Waves South China Sea
2015/7/13
Nonlinear internal solitary waves generated within Luzon Strait move westward across the northern South China Sea, refract around Dongsha Atoll, and dissipate on the Chinese continental shelf after a ...
7th South China Sea Tsunami Workshop, Taiwan, China
China Sea Tsunami Workshop Taiwan China financial
2014/11/3
The 7th South China Sea Tsunami Workshop (SCSTW-7) will be held on November 17-22, 2014 at National Museum of Natural Science, Taichung, Taiwan, China. As one of the SCSTW-7′s sponsors, BICTAM is plea...
Trace metal cycling in the deep water of the South China Sea: The composition, sources, and fluxes of sinking particles
Trace metal cycling in the deep water the South China Sea composition sources fluxes of sinking particles
2014/4/8
Moored sediment traps were deployed for 1 yr at depths of 120, 600, and 3500 m in the water column to investigate the trace metal (M) (Al, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn) composition, sources, ...
Metaproteomic characterization of dissolved organic matter in the water column of the South China Sea
Metaproteomic characterization dissolved organic matter water column South China Sea
2014/4/4
We characterized dissolved organic matter (DOM; < 0.7 μm in size) collected from the surface (10-m and 75-m) and bathypelagic (3000-m) layers in the South China Sea using the shotgun proteomic approac...
The Mekong River plume fuels nitrogen fixation and determines phytoplankton species distribution in the South China Sea during low and high discharge season
The Mekong River plume fuels nitrogen fixation determines phytoplankton species distribution the South China Sea low and high discharge season
2014/4/17
The influence of the Mekong River (South China Sea) on N2 fixation and phytoplankton distribution was investigated during the lowest- and highest-discharge seasons (April 2007 and September 2008, resp...
Characterization of particulate organic matter in the water column of the South China Sea using a shotgun proteomic approach
Characterization of particulate organic matter water column of the South China Sea shotgun proteomic approach
2014/4/17
We characterized particulate organic matter (POM) collected from both the surface (41 m and 200 m) and mesopelagic layers (500 m and 1000 m) in the western South China Sea. By using a shotgun proteomi...
Trace metal cycling in the surface water of the South China Sea: Vertical fluxes, composition, and sources
Trace metal cycling the surface water the South China Sea: Vertical fluxes composition sources
2014/4/16
We deployed floating traps in the surface waters of the South China Sea on four occasions at depths of 30 m,100 m, and 160 m from 2006 to 2007 to quantify vertical metal fluxes in the surface water an...
Altimetry-observed semi-annual cycle in the South China Sea: Real signal or alias of K1 tidal error?
sea level semi-annual cycle satellite altimetry South China Sea
2009/11/17
There have been a number of applications of satellite altimetry to seasonal and interannual sea level variability in the South China Sea. However, these applications usually exclude shallow waters alo...
Close coupling between phytoplankton growth and microzooplankton grazing in the western South China Sea
Close coupling phytoplankton growth microzooplankton grazing
2014/4/18
We conducted 28 dilution experiments during August–September 2007 to investigate the coupling of growth
and microzooplankton grazing rates among ultraphytoplankton populations and the phytoplankton c...
The Nondeterministic Nature of Kuroshio Penetration and Eddy Shedding in the South China Sea
Nondeterministic Nature Kuroshio Penetration Eddy Shedding South China Sea
2008/8/13
A °, 6-layer Pacific version of the Naval Research Laboratory Layered Ocean Model is used to investigate the nondeterministic nature of Kuroshio intrusion and eddy shedding into the South China Sea (S...

